“It has been possible for the first time to scientifically prove that climatic changes have already influenced U.S. thunderstorm losses.”
That’s the statement Munich Re put forth this week when it issued a report stating the correlation between climate change and severe thunderstorm losses in the United States, findings that were based on a 1970-2009 study produced by Munich Re and the German Aerospace Center.
The study examined hail, tornado, thundersquall and heavy rainfall losses throughout the United States, finding that the increase from thunderstorm losses remained, even after adjustments to take into account socio-economi changes.
“It is therefore clear that the change in losses during the period in question is largely driven by changes in climatological boundary conditions,” said Eberhard Faust, from Munich Re’s Geo Risks Research and co-author of the study. “In particular, the potential energy required in the atmosphere for the formation of severe thunderstorms has increased in the course of time.”
This report comes after a record-setting 2011, a year in which thunderstorms and tornadoes caused more than $25 billion in insured losses with 553 direct fatalities., according to theInsurance Information Institute.
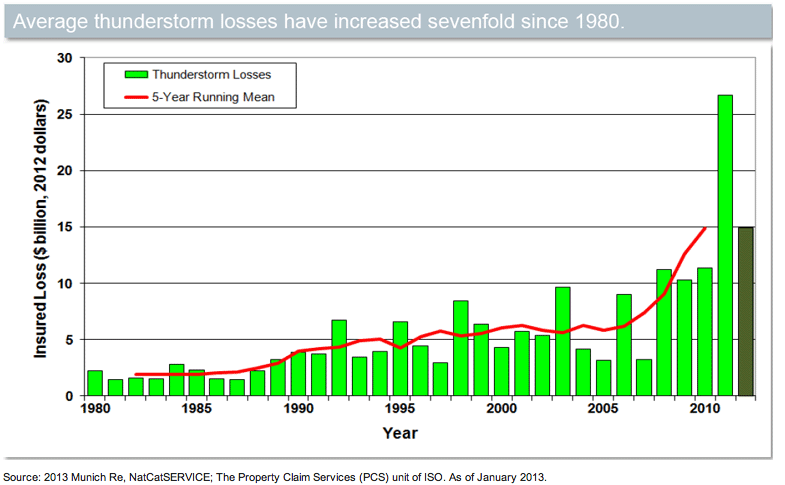
The graph below illustrates U.S. thunderstorm loss trends from 1980 to 2012.
As Dr. Peter Röder, member of Munich Re’s board of management points out, “This scientific study shows, on the one hand, that some regions already need to adapt to changing weather risks. This concerns the insurance industry as risk carrier, first and foremost, but also those in the private and public spheres responsible for deciding on prevention measures.”


 />i
/>i